A dam is a barrier that stops or restricts the flow of surface water or underground streams. Reservoirs created by dams not only suppress floods but also provide water for activities such as irrigation, human consumption, industrial use, aquaculture, and navigability. Hydropower is often used in conjunction with dams to generate electricity. A dam can also be used to collect or store water which can be evenly distributed between locations. Dams generally serve the primary purpose of retaining water, while other structures such as floodgates or levees (also known as dikes) are used to manage or prevent water flow into specific land regions.
Designing and constructing a dam requires analyzing water seepage, filter layer design, dam stability analysis, deformation analysis, and movement analysis for operation and safety. Additionally, maintenance and repairs are necessary due to the dam's wear and tear over time.
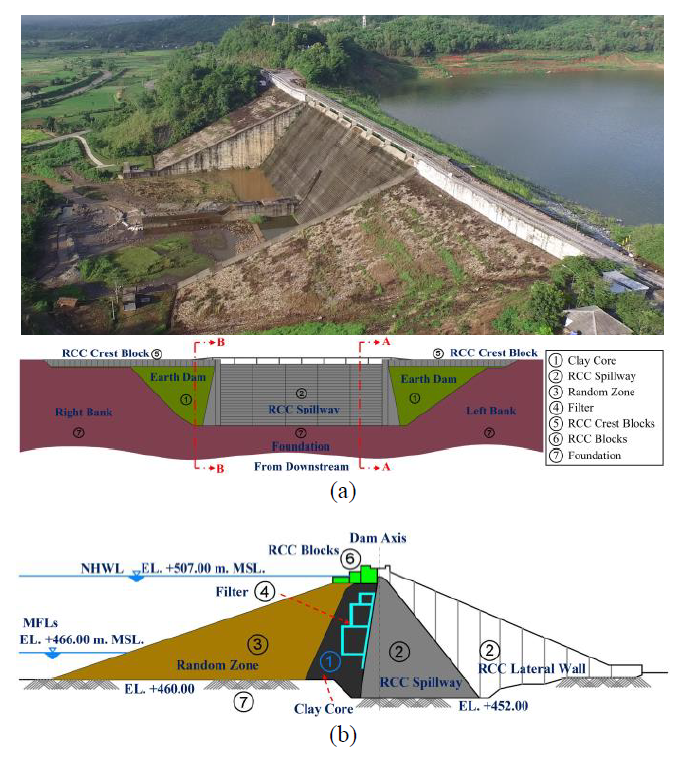
Therefore, in this online training session, we will discuss a case study of dam rehabilitation in Thailand, focusing on the use of the midas GTS NX program
※ The webinar will be conducted in Thai language
Therefore, in this online training session, we will discuss a case study of dam rehabilitation in Thailand, focusing on the use of the midas GTS NX program
※ The webinar will be conducted in Thai language
.png)


/GEN.png?width=600&height=600&name=GEN.png)
/CVL.png?width=600&height=600&name=CVL.png)


