Wind Load as per ASCE 7-16
Information of Example Model
This is an explanation how to input wind load data in the warehouse with monoslope roof.
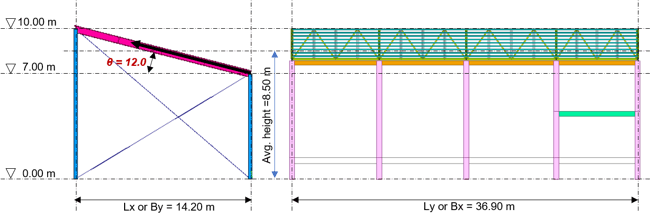
Information of the example model is given as follows.
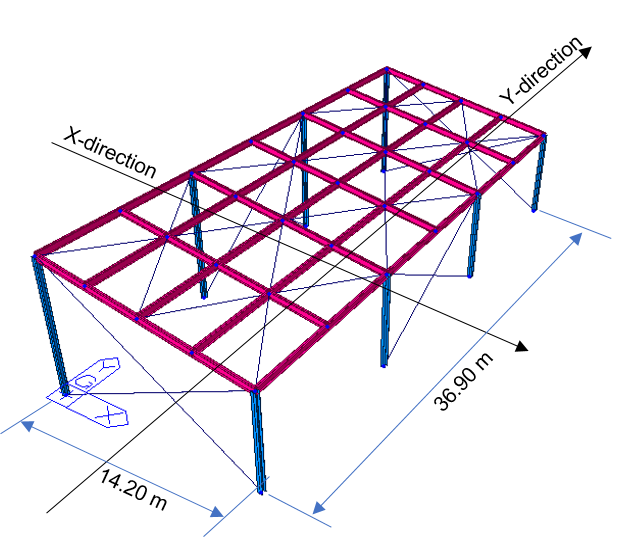
Figure1. Warehouse Example Model

Calculation of Wind Load - Velocity Pressure
The velocity pressure should be calculated in order to get the value of the wind load.
- Velocity Pressure : qz = 0.613KzKztKdKeV2
It usually applies ' 1.0 ' on the Ground Elevation Factor, Ke, if there is no exceptional case caused.
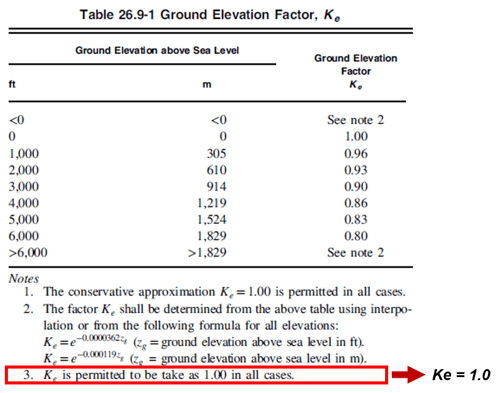 Figure 3. Ground Elevation Factor
Figure 3. Ground Elevation Factor
2) Determination of Kd (Wind Directionality Factor)
It applies ' 0.85 ' since the wind directionality factor is based on the structure.
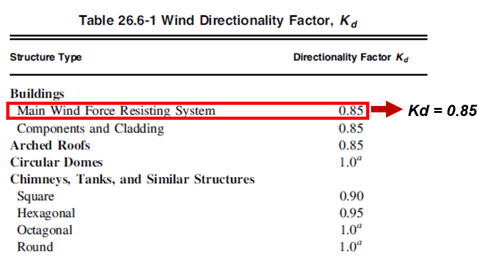 Figure 4. Wind Directionality Factor
Figure 4. Wind Directionality Factor3) Determination of Kz (Velocity Pressure Exposure Coefficient)
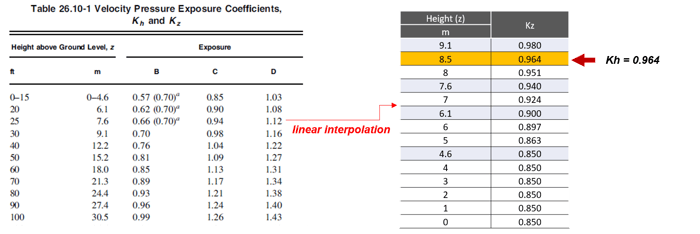
4) Determination of Kzt (Topographic Effects)
-
Kzt = (1+K1K2K3)2
-
Assumed ValuesHill Type : 2S Escarpment
H = 20m, Lh = 40m, x = 40m → H/Lh = 20/40 = 0.5, x/Lh = 40/40 = 1.0
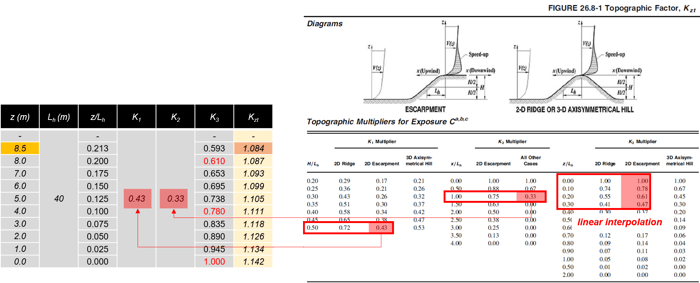 Figure 6. Determination of Topographic Effects
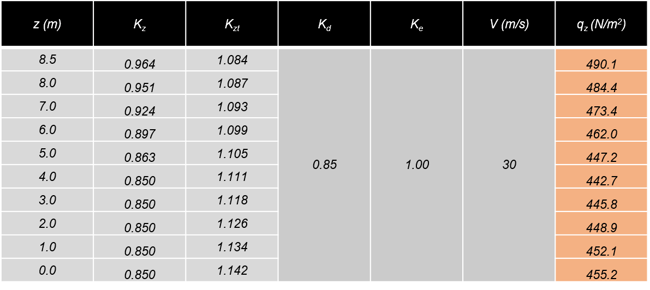
Figure 6. Determination of Topographic Effects5) Determination of qz and qh
The following is a table that indicates the final value of the velocity pressure after calculating values for all variables. To calculate wind pressure, qh value for the roof level is applied.
Applying the pressure value depending on levels is more exact, but, it is okay to put the load value by using only the value of qh instead.
-
Velocity Pressure : qz = 0.613KzKztKdKeV2 ≈ 490N/㎡ =qh
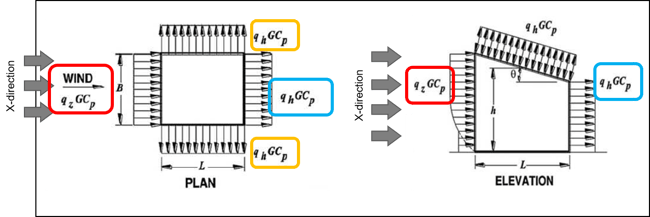
Calculation of Wind Load - External Wind Pressure
p = qGCP - qi(GCpi)
Case 1) Wind Pressure = External Wind Pressure - Internal Wind Pressure (Positive)
Case 2) Wind Pressure = External Wind Pressure - Internal Wind Pressure (Negative)
Two coefficient values for external pressure and internal pressure are needed in order to satisfy the formula. Basically, wind pressure has two values depending on the direction of internal pressure. If internal pressure is larger than the external pressure, positive internal pressure is generated. In the opposite case, negative internal pressure is generated.
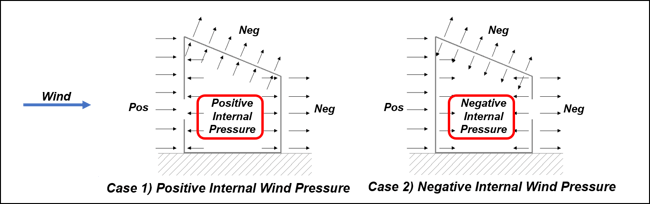 Figure 7. Positive Internal Wind Pressure and Negative Internal Wind Pressure
Figure 7. Positive Internal Wind Pressure and Negative Internal Wind Pressure
1) External Wind Pressure for Gable Roof Direction
Wind ward wall, leeward wall, and side wall are needed to satisfy the calculation of external wind pressure.
The following is an explanation of the calculation for the x-direction and wall.
• Gust Factor (G) = 0.85 (Assumed Value)
* You can get the gust factor as per 26. 11. 4
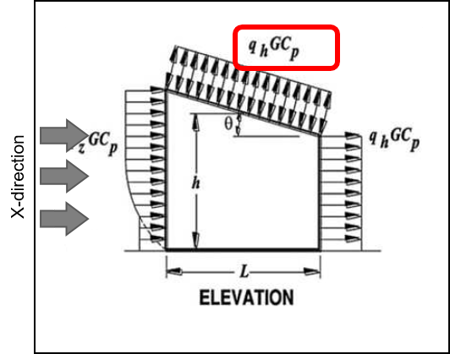
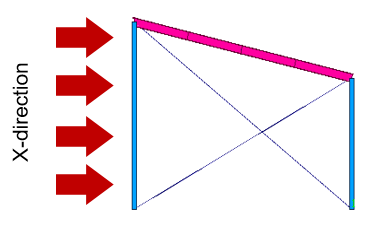 Figure 8. External Wind Pressure in X-Direction
Figure 8. External Wind Pressure in X-Direction
• Wall Pressure Coefficients (Cp)
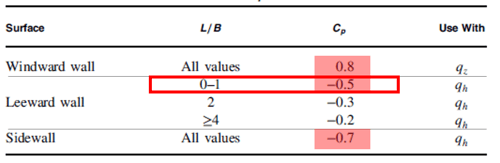 Figure 9. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 1
Figure 9. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 1
* L/B =14.2 / 36.9 = 0.385
Red Box : Wind load for windward wall (Wx(+ or -)_Windward)
q_wind = qzGCP = 490 * 0.85 * 0.8 = 333.2 N/m2
Blue Box : Wind load for Leeward wall (Wx(+ or -)_Leeward)
q_lee = qhGCP = 490 * 0.85 * - 0.5 = -208.3 N/m2
Yellow Box : Wind load for Side wall (Wx(+ or -)_Side)
q_side = qhGCP = 490 * 0.85 * - 0.7 = -291.6 N/m2
The following is an example of the calculation for the roof in X-Direction.
• Gust Factor (G) = 0.85 (Assumed Value)
* You can get the gust factor as per 26. 11. 4
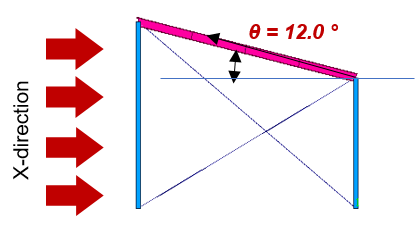 Figure 11. External Wind Pressure for the Roof in X-Direction
Figure 11. External Wind Pressure for the Roof in X-Direction
• Roof Pressure Coefficients, Cp, for use with qh
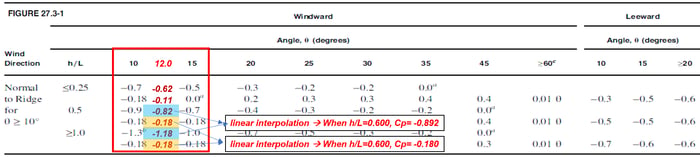
Red Box : Wind load for windward roof (Wx(+ or -)_Windward)
q_wind = qzGCP = 490 * 0.85 * -0.763 = -324.273 N/m2
q_wind = qzGCP = 490 * 0.85 * -0.152 = -64.6 N/m2
2) External Wind Pressure for Gable Roof Orthogonal Direction
The following is an explanation of the calculation for the y-direction. The wall pressure for the y-direction can be calculated as the x-direction way.
• Gust Factor (G) = 0.85 (Assumed Value)
* You can get the gust factor as per 26. 11. 4
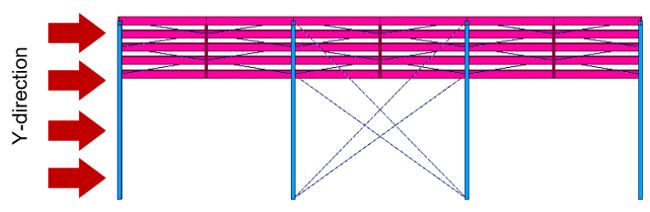
• Wall Pressure Coefficients (Cp)
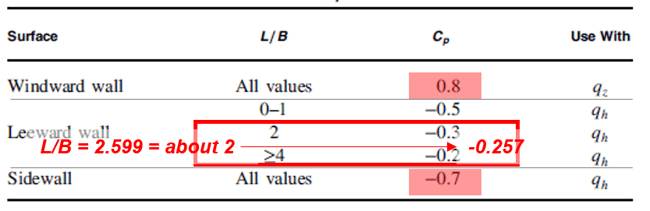 Figure 15. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 1
Figure 15. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 1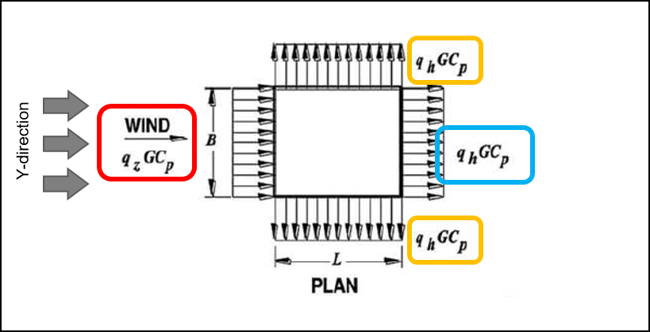 Figure 16. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 2
Figure 16. Wall Pressure Coefficients - 2Red Box : Wind load for windward wall
q_wind = qzGCP = 490.1 * 0.85 * 0.8 = 340 N/m2
Blue Box : Wind load for Leeward wall
q_lee = qhGCP = 490.1 * 0.85 * -0.257 = -107.1 N/m2
Yellow Box : Wind load for Side wall
q_side = qhGCP = 490.1 * 0.85 * -0.7 = -297.5 N/m2
The following is an example of the calculation for the roof in Y-Direction. For the roof in slope and orthogonal direction, it should be considered as "0".
• Gust Factor (G) = 0.85 (Assumed Value)
* You can get the gust factor as per 26. 11. 4
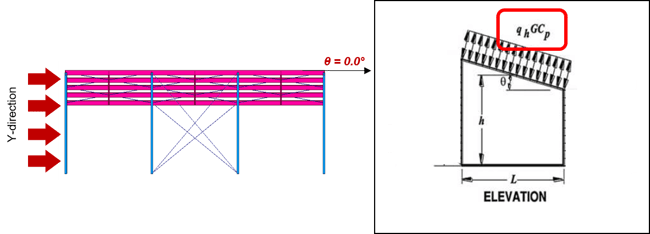 Figure 17. External Wind Load in Y-Direction and Angle
Figure 17. External Wind Load in Y-Direction and Angle
* h = 8.5m, Lx = 36.9m → h/L = 0.230
q_wind = qzGCP = 490 * 0.85 * -0.9 = -374.9 N/m2
q_wind = qzGCP = 490 * 0.85 * -0.18 = -75.0 N/m2
• Roof Pressure Coefficients, Cp, for use with qh

Figure 18. Roof Pressure Coefficients
Calculation of Wind Load - Internal Wind Pressure
1) Internal Wind Pressure for Gable Roof Orthogonal Direction
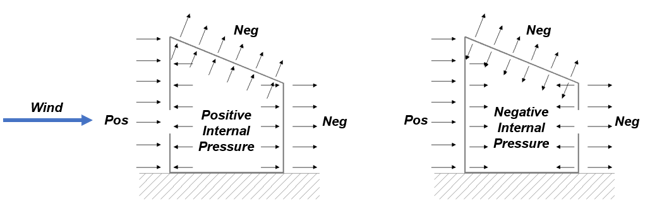 Figure 19. Internal Wind Pressure for Gable Roof Orthogonal Direction
Figure 19. Internal Wind Pressure for Gable Roof Orthogonal DirectionPartially enclosed buildings in enclosure classification would be applied in this example. Therefore, the value of the internal pressure coefficient can be assumed as +0.55 and -0.55.
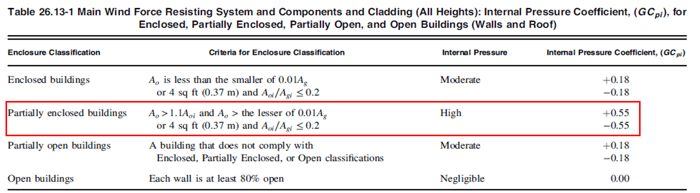 Figure 20. Table for Internal Pressure Coefficient
Figure 20. Table for Internal Pressure Coefficient
2) Wind Pressure on Wall for Gable Roof Direction (along x-direction)
Wind pressure in the x-direction is given as follows. The values of each case in the wind pressure are calculated by applying the values of the external pressure and internal pressure.
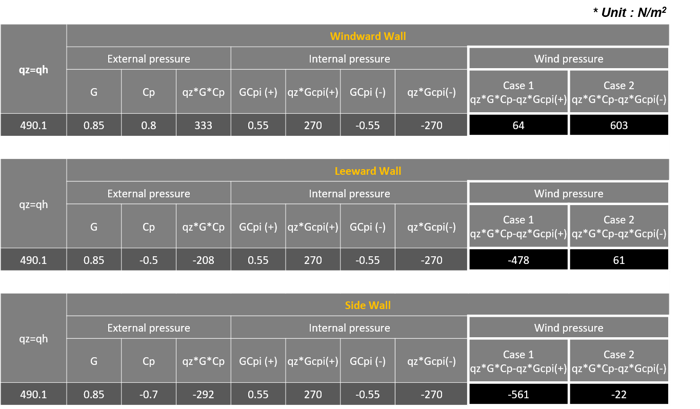 Table 3. Wall Wind Pressure Values along X-Direction
Table 3. Wall Wind Pressure Values along X-Direction
3) Wind Pressure on Roof for Gable Roof Direction (along x-direction)
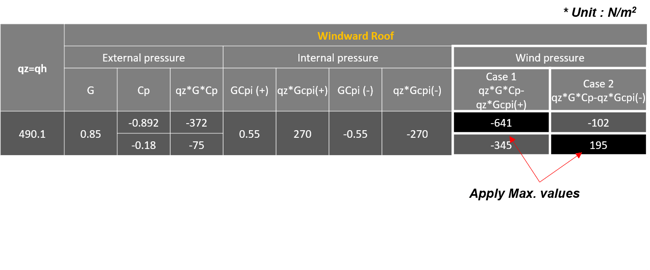 Table 4. Roof Wind Pressure Values along X-Direction
Table 4. Roof Wind Pressure Values along X-Direction
4) Wind Pressure on Wall for Gable Roof Orthogonal Direction (along y-direction)
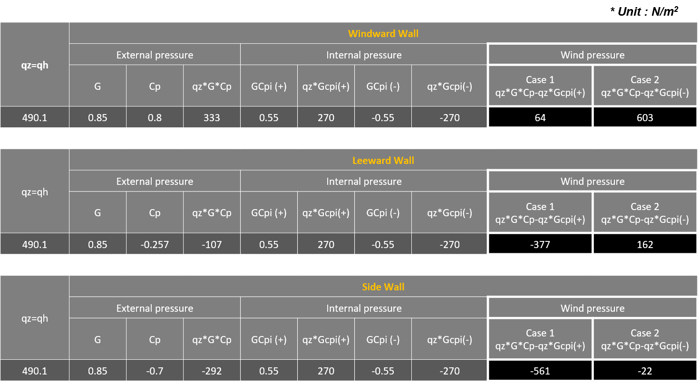 Table 5. Wall Wind Pressure Values along Y-Direction
Table 5. Wall Wind Pressure Values along Y-Direction
5) Wind Pressure on Roof for Gable Roof Orthogonal Direction (along y-direction)
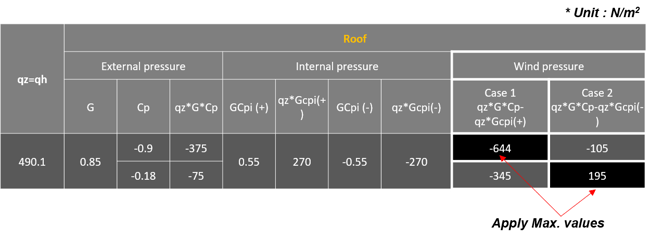 Table 6. Roof Wind Pressure Values along Y-Direction
Table 6. Roof Wind Pressure Values along Y-Direction
Wind Pressure Summary
The final values for cases 1 & 2 are as follows.
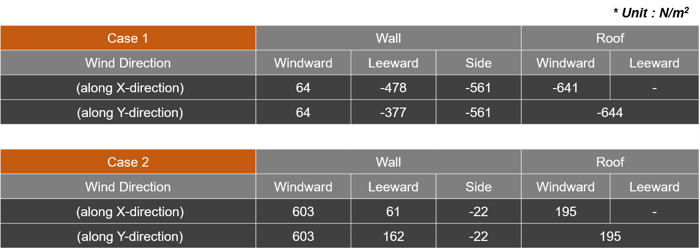 Table 7. Values for Cases 1 and 2
Table 7. Values for Cases 1 and 2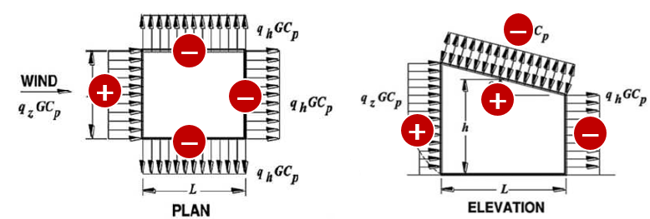
• Sign (+) : Direction to the inside of the building
• Sign (-) : Direction to the outside of the building
Input a Wind Load
1) Create Load Cases for the Wind Load
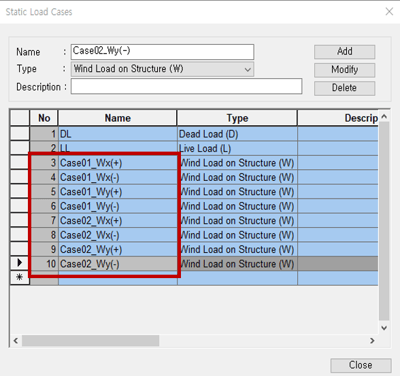 Figure 22. Static Load Cases Dialog Box
Figure 22. Static Load Cases Dialog Box* Tips : you can easily distinguish each case if you put the name above.
Considered Factors
- Case : Case 1 & Case 2
- Wind Direction : X-Direction & Y- Direction
- Wind Sign : (+) & (-)
2) Create a Floor Load Cases for Wind Load
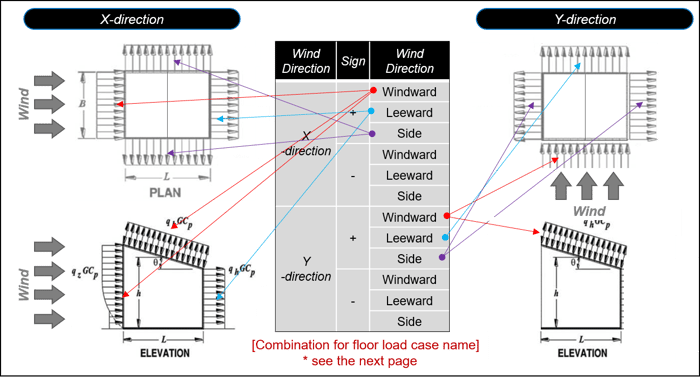 Figure 23. Information of Floor Load Cases for Wind Load
Figure 23. Information of Floor Load Cases for Wind Load
3) Input Wind Load as a Floor Load
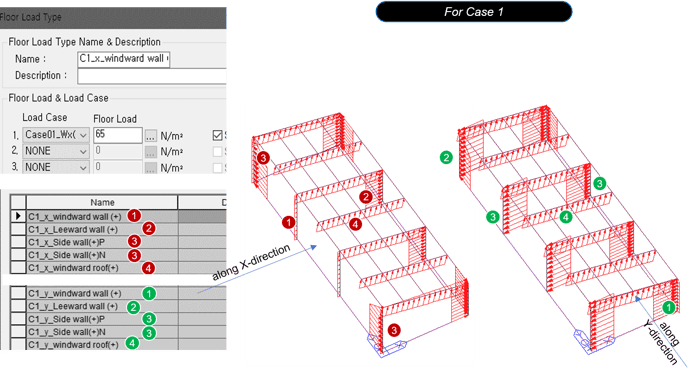 Figure 24. Floor Load Type Dialog Box for Case 1
Figure 24. Floor Load Type Dialog Box for Case 1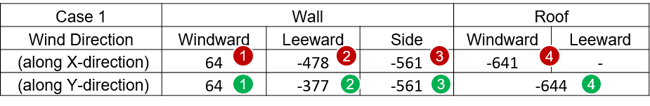 Table 8. Case 1 Values of Wall and Roof
Table 8. Case 1 Values of Wall and Roof• Sign (+) : Direction to the inside of the building
• Sign (-) : Direction to the outside of the building
When inputting the wind load into the model, the sign must be corrected according to the direction of the load.
It also creates a floor load type for the opposite direction.
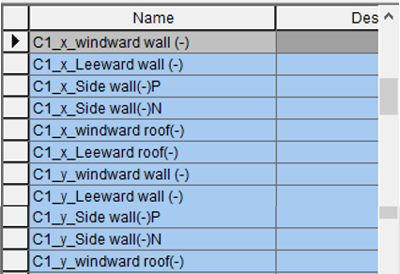
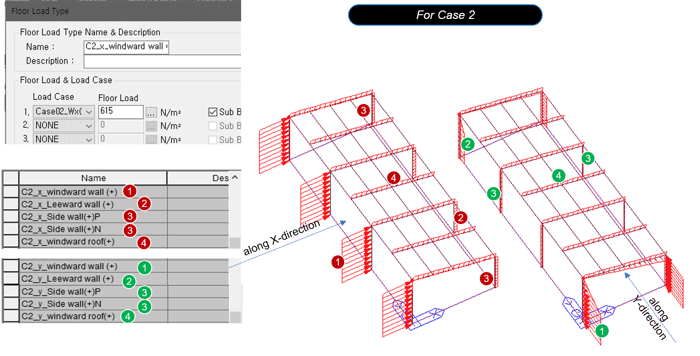 Figure 26. Floor Load Type Dialog Box for Case 2
Figure 26. Floor Load Type Dialog Box for Case 2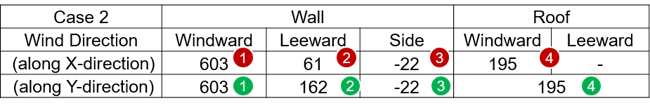
Table 9. Case 2 Values for Wall and Roof
• Sign (+) : Direction to the inside of the building
• Sign (-) : Direction to the outside of the building
When inputting the wind load into the model, the sign must be corrected according to the direction of the load.
It also creates a floor load type for the opposite direction.
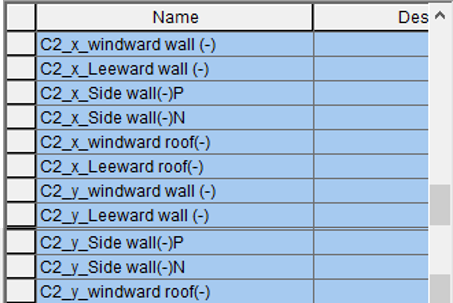 Figure 27. Case 2 Name List Dialog Box
Figure 27. Case 2 Name List Dialog Box
4) Generate Load Combinations with a Wind Load
Before performing analysis and design, we recommend you make load combinations with a wind load. Even if it is not automatically generated, you can easily create it by using a table for the load combination or copying it from excel.
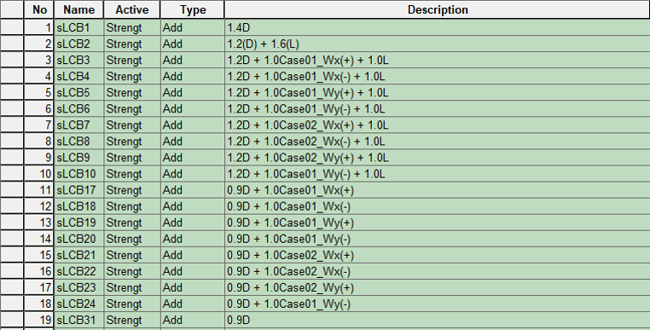 Figure 28. Load Combination Example - 1
Figure 28. Load Combination Example - 1 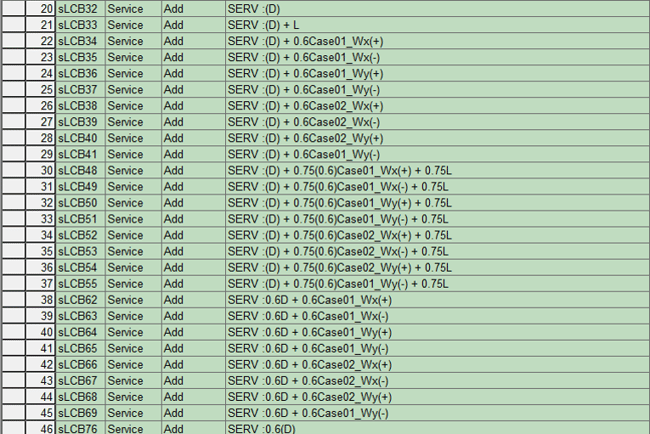 Figure 29. Load Combination Example - 2
Figure 29. Load Combination Example - 2





