Material properties must be applied when performing analysis. midas Civil provides 'Material Properties' function to define various materials. Some users who are a beginner or are not familiar with midas Civil might be confused while defining a material property because there are various options. These options are used for linear analysis or nonlinear analysis and those are used or not depending on the purpose of analysis.
In this session, we will introduce the meaning of each option and how to use it more effectively. We hope you use 'Material Properties' function properly.
This content highlights
1. Basic Tutorial about 'Material Properties' function
Material Property is a necessary factor for analysis. We will see the basic options and usages of 'Material Properties' function.
2. Useful Tips for Using 'Material Properties' function & FAQs
We have different projects that have the same material properties sometimes. We will see useful tips to avoid repeated works. And also, we will look into additional options and frequently asked questions regarding material properties.
3. 'Material Properties' Function for Advance analysis
'Material Properties' function has additional options for non-linear analysis as well as linear static analysis. Let's see the options and how to apply the options.
1. Basic Tutorial about 'Material Properties' function
We can define material properties using 'Material Properties' function easily. It has material data for each national design code and also a space for user-defined material. Here are steps to define material properties.
1. Enter ID number and Name.
2. Select a type of design after that, select a standard and material data.
3. In Type of Material, Isotropic or Orthotropic can be selected.
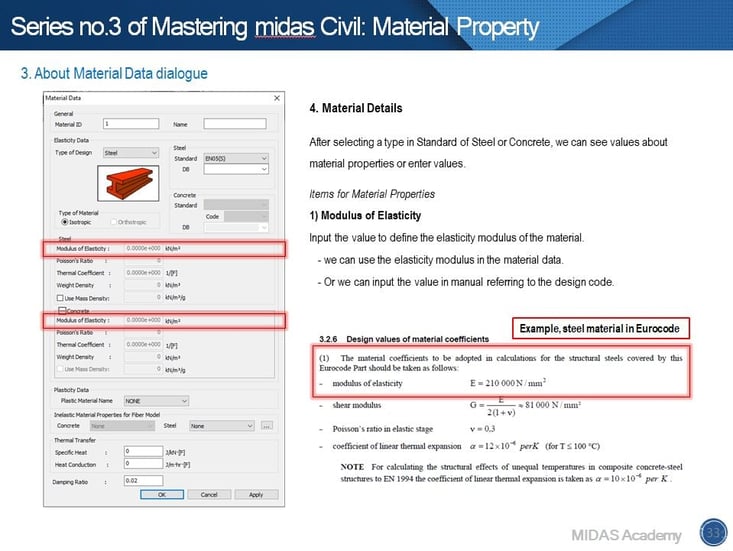
4. Enter the mechanical properties of the material such as Elasticity modulus, Poisson's Ratio,
Thermal Coefficient, and Weight Density.
5. Lastly, check 'Use Mass Density' option to consider the mass for Eigenvalue analysis.


2. Useful Tips for Using 'Material Properties' function & FAQs
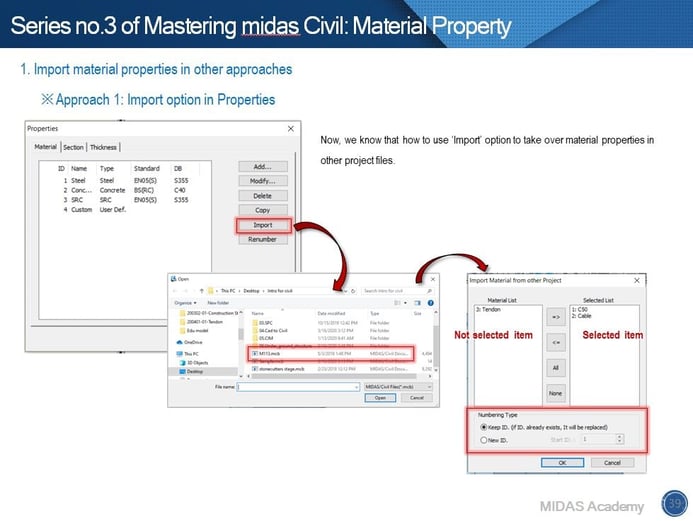
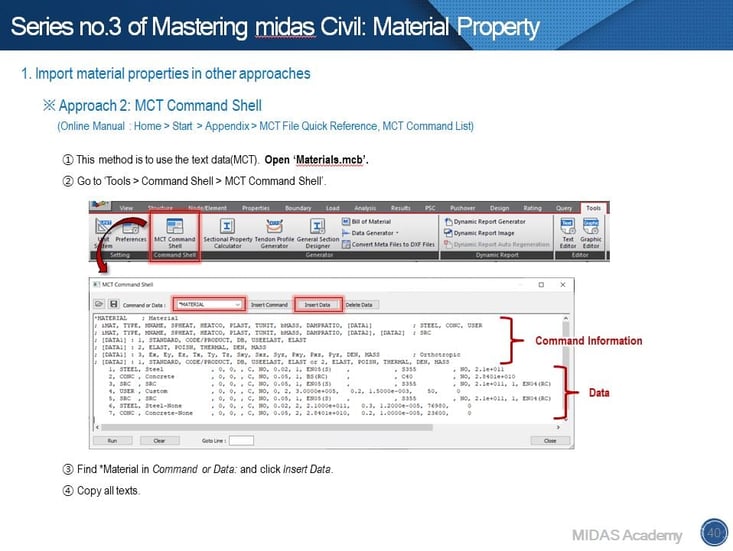
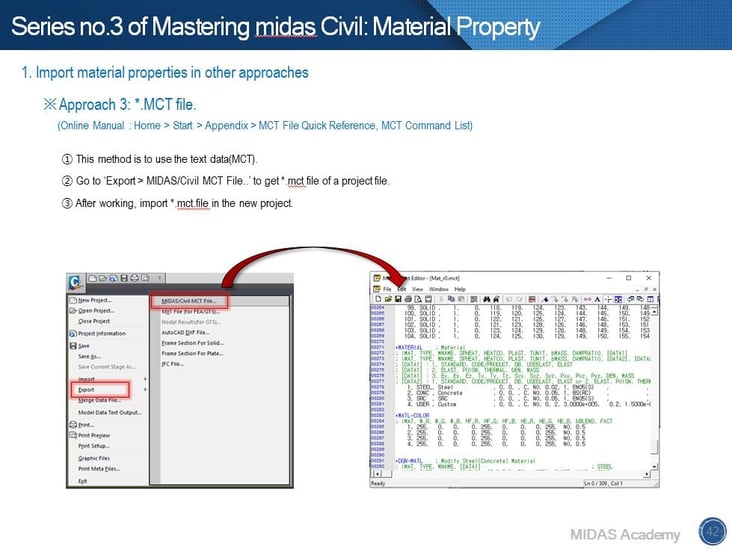
Do you have experience doing something repeatedly to define the same materials? midas Civil provides several ways to reduce time. That is the Import option. In order to import material data from other models, we can use three options. Especially, you can use texts to manage material data or others using no.2 and no.3 approaches.
1. Import option in Properties dialogue.
2. Use MCT Command Shell.
3. Use *.mct file.
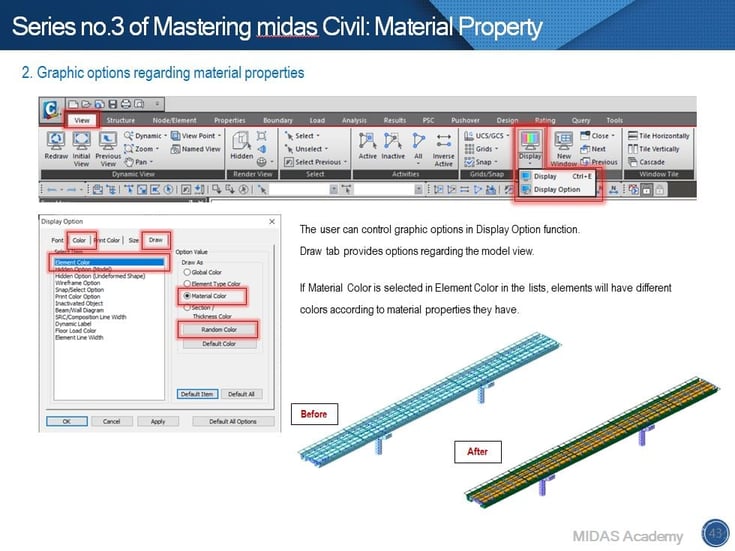
The display option gives you different color types for element models.
FAQs session regarding material properties.
Q1. Why does the design report show different modulus of elasticity?
The modulus of elasticity in Material Data isn’t used.
A1. The key is None type in Standard. If the None type is selected, we should enter values to define a material property for design calculation. Based on the entered value, material properties will be calculated.

Q2. Why do we select material properties again when we define Composite or SRC section?
A2. Composite and SRC section is a section made up of two different materials for enhancing mechanical properties. In order to simplify the calculation for section properties of a composite section, the ratio of material properties is used.

Q3. Which material should I assign to the element if I have many material properties and have the construction stage analysis?
A3. Case 1: Construction Stage Analysis(X), Composite Section(O)
In this case, assign the material property of part1 to elements that have the composite section property. The material property of part 2 will be calculated by using the ratio inputted in the composite section property. Therefore, it is important to select materials desired in the composite section property in order to obtain the expected results.

Case 2: Construction Stage Analysis(O), Composite Section(O)
In this case, we don’t care about what material is assigned if the Composite Section for Construction Stage option is defined. When we consider the construction stage analysis, Composite Section for C.S function helps us assign different material properties to part 1 and part 2 of the composite section. Based on selected materials, the section properties of the composite section will be re-calculated and used for the analysis.

3. 'Material Properties' Function for Advance analysis
In this webinar, we had skimmed material properties for advance analysis.
1. Plastic Material Properties
This option is used to consider the plastic material behaviors of the model. You can check permanent or irreversible deformations that occur in the structure in plastic behaviors. In order to select a plastic material, you need to define the plastic material in the Plastic Material function.
2. Inelastic Material Properties for Fiber Model
This option is used to assign the concrete and steel material to the Fiber Section.
Fiber Model or Fiber element is used for Nonlinear Analysis. Inelastic material properties will be assigned to cells of the section that are divided by Fiber Division of Section function. Fiber Model discretizes the section of beam elements into cells. And each cell is able to have each material property to consider the inelastic characters of each material in one section. We can consider this option for the non-linear seismic analysis which includes inelastic material properties.

3. Thermal Transfer
Specific Heat and Heat Conduction under Thermal Transfer option is regarded as the Heat Transfer Analysis and Thermal Stress Analysis.
You can find those values in Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Materials.
Specific Heat: Specific heat capacity
Heat Conduction: Thermal conductivity
These inputs will be used for Heat of Hydration function.

4. Damping Ratio
The damping Ratio in material properties is used to define Group Damping. The group Damping function assigns the same damping ratio as per materials, sections, and boundaries. (Path: Properties > Damping > Group Damping)
For the response spectrum analysis: Select Strain Energy Proportional in Damping Method.
For the time history analysis: Select Element Mass & Stiffness Proportional in Damping Method or Strain Energy Proportional in Damping Method.

Watch the full webinar video