Beam Bridges: An Essential Element in Transportation Infrastructure
Beam bridges, commonly referred to as girder bridges, represent one of the most prevalent and fundamental bridge types globally. Despite their apparent simplicity, these structures play a pivotal role in our transportation systems, ensuring the safe passage of vehicles and pedestrians across various terrains such as rivers, valleys, and highways. This article delves into the design, construction, and essential features of beam bridges, highlighting the science behind their stability and strength.
1. What Are Beam Bridges?
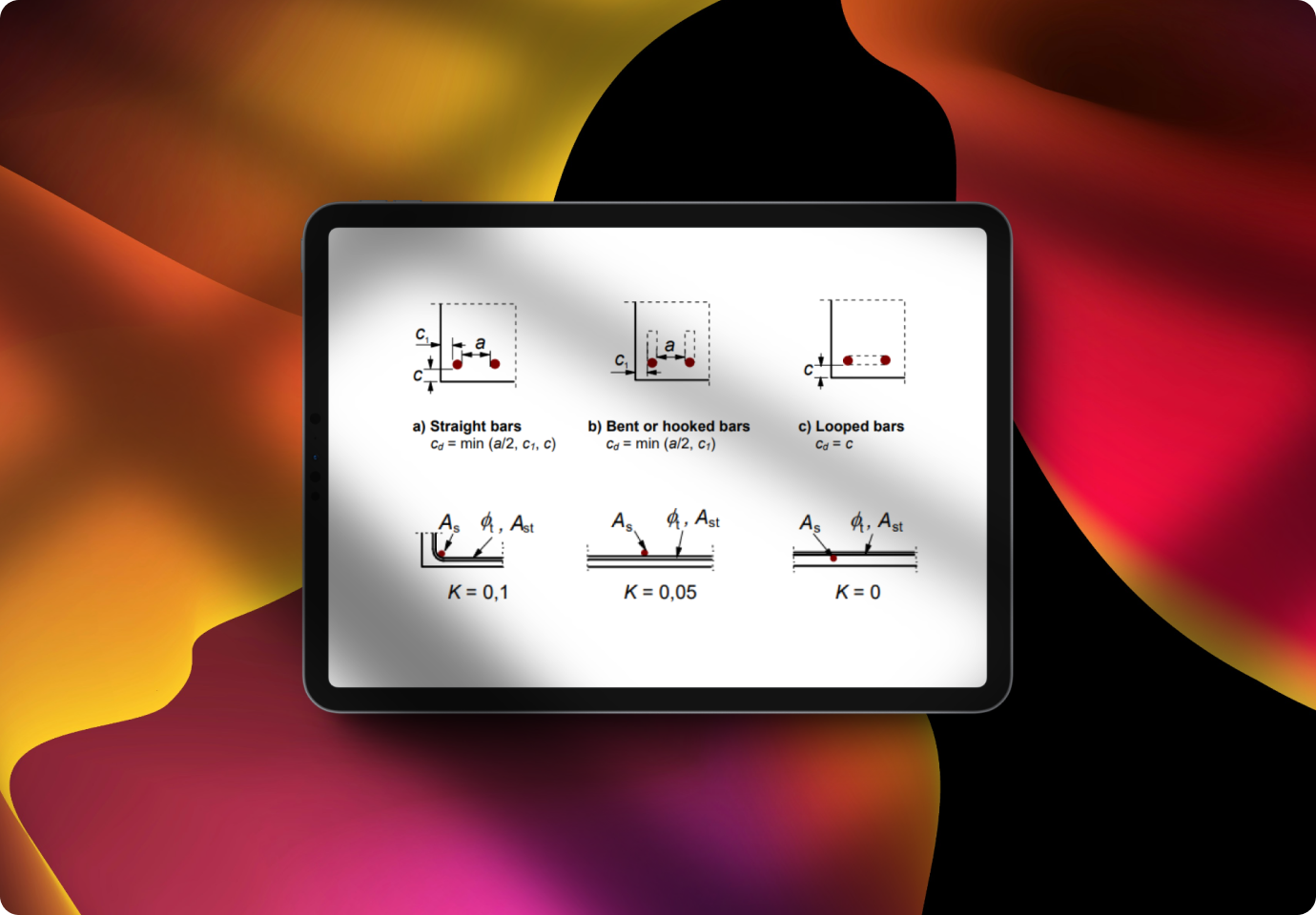
A beam bridge consists of one or more horizontal beams that are supported at their ends by piers or abutments. These concrete elements may be reinforced, pre-tensioned, or post-tensioned. Modern variations include girder, plate girder, and box girder bridges, all falling under the beam bridge category.
Construction methods vary, ranging from multiple beams placed side by side with a deck on top to a main beam on each side supporting a central deck. The main beams can be I-beams, trusses, or box girders, designed as either half-through or fully braced to form a through bridge.
2. Components of a Beam Bridge
Beams (Girders)
The beams are the primary load-bearing components, extending longitudinally across the span. These can be constructed from wood, steel, concrete, or a combination, with the choice influenced by factors like span length, expected load, and environmental conditions.
Supports
Beam bridges utilize supports such as piers or abutments to bear the beams' load and transfer it to the ground. Piers are vertical structures built in water or on land, while abutments are solid supports located at the bridge’s ends.
Deck
The deck is the surface used by vehicles and pedestrians. Positioned atop the beams, the deck’s material and design depend on the bridge’s intended use and location.
Substructure
The substructure includes all elements below the deck that aid in load distribution and support. This comprises the pier cap, pier, pile cap, pile, and abutment.

3. Beam Bridge Design Principles
Bending and Compression Forces
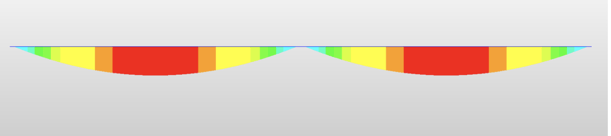
Beam bridges primarily contend with bending and compression forces. When a load is applied to the bridge deck, the beams bend, causing compression at the top and tension at the bottom. Engineers select materials and dimensions that ensure the beams can safely withstand these forces.
Span Length
The span length is crucial in beam bridge design. Short spans are simpler, typically single-span bridges, whereas longer spans may necessitate multiple spans or advanced engineering solutions to manage bending and compression forces effectively.
Material Selection
Material choice is influenced by factors such as load-bearing capacity, environmental conditions, and cost. Steel and concrete are popular for their strength and durability, with concrete preferred for shorter spans and steel for longer ones.
Load Analysis
Engineers must estimate the maximum loads the bridge will face, including traffic, live loads (pedestrians and vehicles), and environmental impacts like wind and seismic activity. This data informs the design of the bridge's beams and supports.
Support Placement
Strategic placement of supports is vital for load distribution and stability. Engineers consider terrain, water currents, and geological conditions to determine optimal locations for piers or abutments.
Safety Considerations
Safety is paramount, with designs incorporating guardrails, railings, and other protective measures to prevent accidents and enhance user safety.
4. Beam Bridges - Construction Methods
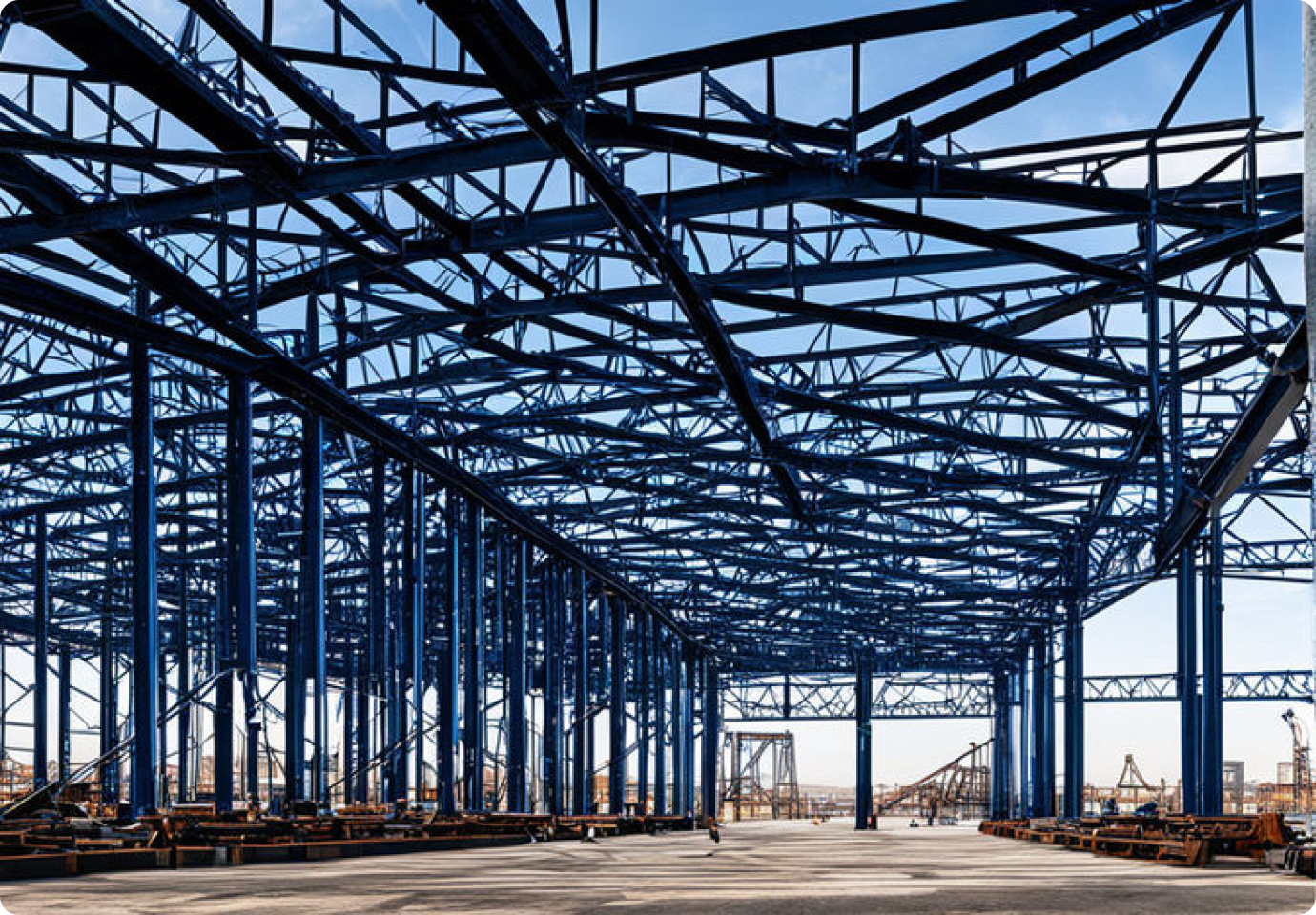
Precast Beams
Often, bridge beams are precast off-site and transported to the construction site for installation using cranes. This method reduces construction time and minimizes traffic disruptions.
 Picture 2: Precast beam sections
Picture 2: Precast beam sections
Cast-in-Place Beams
For smaller bridges or where precast beams are impractical, cast-in-place methods are used, involving concrete poured into molds on-site. This technique, though more time-consuming, offers greater design flexibility.
 Picture 3: Bridge Beams
Picture 3: Bridge Beams
5. Types of Beam Bridges
Beam bridges are classified based on various criteria:
Geometry:
- Straight beam
- Curved beam
- Tapered beam
Cross-Section Shape:
- I-beam
- T-beam
- C-beam
- Box
Support Type:
- Simply supported beam
- Cantilever beam
- Continuous beam
- Fixed beam
6. Conclusion
Beam bridges, despite their simplicity, are integral to transportation infrastructure, offering efficient solutions for short and medium spans. Their design principles, material selection, and construction methods are critical for ensuring safety and durability, providing reliable and cost-effective ways to overcome various obstacles in our built environment.